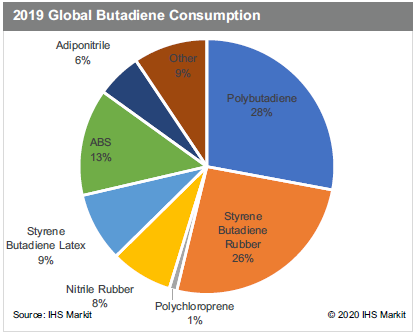
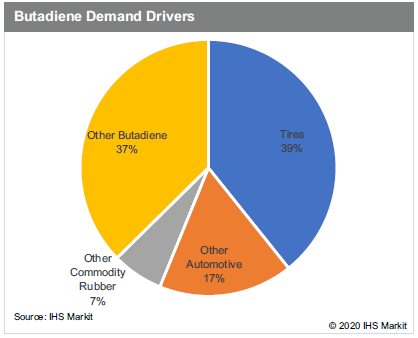
Industrial ImpactCOVID-19 is impacting every single sector of global industry. The airline industry is struggling with the substantial decrease in the number of passengers and flights. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) estimated a 9- 23% decrease in the number of passengers flying, depending on region, even before the rapid spread of COVID-19 in Europe and the US. European countries are blocking borders and reducing the number of flights in and out in order to prevent further spread. The estimated impact on passenger numbers is likely to grow even further from the table shown. It is estimated that airplane tires are required to be replaced after roughly 300-400 take-offs and landings. With the number of flights being substantially reduced because of COVID-19, demand for both synthetic and natural rubbers will decrease as well. Further restrictions on air travel are possible around the globe and will likely further reduce demand for rubber. Aside from rubber demand, all other petrochemical demand associated with the airline industry is likely to decrease, especially demand for plastics associated with packaging and inflight services like meals and drinks. Tire demand is divided into two segments: original equipment (OE) and replacement equipment (RE). The OE segment accounts for roughly 25% of global tire demand, while the RE segment accounts for the rest. The reduction in the light vehicle production forecast will decrease demand for the OE tire segment. This is only 25% of total tire demand, but COVID-19 will also have an impact on RE segment tire demand as people are required to stay home, businesses require employees to work from home, and blockades are placed between countries, provinces, and cities to prevent the spread of the virus. These measures will eventually have a big impact on demand for rubber as well as butadiene. Over half of butadiene demand is driven by tire and automotive industries. Large butadiene derivatives like polybutadiene rubber and styrenebutadiene rubber are key components of producing tires and other auto parts like belts, hoses, and gaskets. Some ABS demand also comes from the production of auto parts. These three derivatives account for roughly three-fourths of global butadiene demand. Significant demand decreases from the tire and automotive industries will pressure butadiene demand and price. COVID-19 is continuing to spread around the globe and is likely to further impact demand for butadiene and rubbers. The ultimate magnitude of the impact on C4s and rubbers is still too early to predict at this stage, but the impact is expected to increase until COVID-19 is contained globally.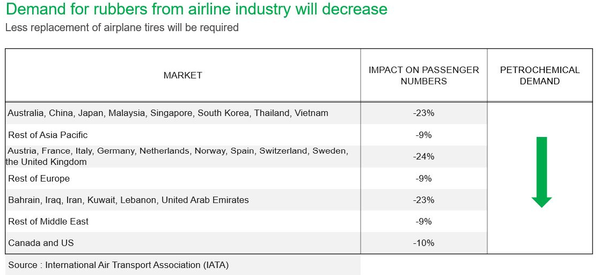
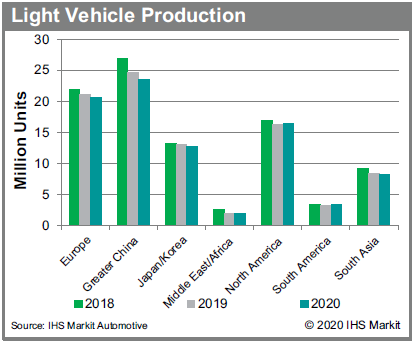
Far more concerning is the automotive industry. The automotive industry was already impaired when COVID-19 started rapidly spreading within China. China accounts for roughly one-fourth of global light vehicle production and manufacturing sites had to be shut down amid labor shortages, province lockdowns, and logistic problems. This was not only a problem for China, but also for automotive manufacturers in other countries as well. Automotive manufacturers who relied on auto part imports from China were also impacted. Several manufacturers had to reduce production rates or even shut down for a few days because of low auto part inventory.
According to IHS Markit Automotive, the global light vehicle production forecast is around 87.2 million units for 2020, which was forecast before the rapid spread of COVID-19 in Europe and the US. This year's production forecast is lower than 2014 production levels. Global automotive production growth rates were -1.0% in 2018 and -5.6% in 2019. Global automotive production growth was expected to be -1.9% in 2020, but it is a near certainty that the growth rate will be much lower than pre-COVID-19 views.