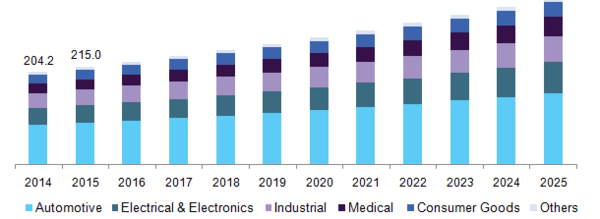
The global thermoplastic polyester elastomer (TPEE) market size was estimated at USD 845.2 million in 2016. Rising substitution of thermosets and other conventionally heavy materials such as metals and wood is expected to remain a key driving factor for the industry over the forecast period. The industry has remained a relatively niche segment in the global thermoplastic elastomers market, on account of low manufacturer & consumer awareness and the vast platform of homopolymers and copolyester types included under the overall umbrella of TPEs. However, these small family of high-performance plastics are rapidly gaining attention in the industry owing to good dimensional stability, and high stiffness among other properties. U.S. TPEE market revenue by end-use, 2014 - 2025 (USD Million) Other uncertainties in the industry arise from differing brand names among numerous suppliers and lack of knowledge regarding the exact applications of each TPE type. Additionally, the polyester supply chain has also witnessed numerous restructuring and divestment activities owing to supplier discrepancies. These factors have hampered industry growth to some extent. However, the ability of all TPEs to process in a manner similar to thermoplastics and imitate the texture & performance of thermoset rubbers has made them ace demanding application trials over the last decade. TPEE products are also gaining favor on account of their faster processing & lower scrap or wastage rates. Engineering applications necessitate a fine equilibrium between performance & cost. Mechanical, electrical, thermal, and other physical properties determine the selection of polymers, which is either polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). PBT elastomers are particularly well-suited to injection molding, and consequently the process is responsible for a majority of its consumption. TPEE is also consumed in extrusion processes, typically for cable & wire or fiber optics. PET similarly possesses excellent color stability, creep even at elevated temperatures and wear properties. Around 90% of resins are compounded with reinforcements, fillers, and other additives. This blurs the distinction between base resin properties of each polymer, yet the process is also responsible for technological developments in FDA-acceptable and flame-retardant blends. Novel alloys combining the properties of polyesters with polycarbonates have also been developed and may witness widespread commercialization over the forecast period. Regulatory agencies play a crucial role in formulating processing guidelines, standardizing reins properties & quality and ensuring consumer safety among other factors. Bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. Food & Drug Administration, National Sanitation Foundation, Underwriter’s Laboratory and others are a few associations responsible for regulating & standardizing such products, while also controlling pollution and emission levels.